Preparation and Functional Detection of Spirulina Suspension Oral Liquid
Abstract: A functional oral liquid was prepared with spirulina. Based on the single-factor experiment, process parameters of preparation of spirulina oral liquid were optimized. The results showed that the fermentation temperature was 30℃ and the time was 2h, and the spirulina flavor could be removed. Add honey 3%, sugar sweet-scented osmanthus 1%, sucralose 0.0067%,citric acid 0.025%, get the best taste, with spirulina fermentation after the unique fragrance. WitH sodium carboxymethyl cellulose 0.12% , xanthan gum 0.08%, propylene glycol alginate 0.06% compound stabilizer, good stability, uniform suspension and blue-green stability. The detection rate of UHT pre-phycocyanin was 0.955mg/mL, 0.790mg/mL after UHT, and the loss rate was 17.26% and the functional loss rate was 20%.
Keywords: spirulina;oral solution;phycocyanin;stability;functional testing
KONG Yu,ZAN Ke,QIN Jia-ting,CHEN Xue-yun
(Engineering Research Center of Food Biotechnology,Ministry of Education, Tianjin University of Science & Technology, Tianjin 300457, China)
Spirulina is a class of lower plants, belonging to the cyanobacterial phylum, phyla, like bacteria, there is no real nucleus in the cells, so also known as cyanobacteria [1]. In 1974, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) conference identified Spirulina as “one of the best protein sources” and “the most desirable food for all mankind .” The study found that spirulina with long-term supplementation of more than 5% had no toxic side effects in vivo and in vitro [2], the crude protein in Spirulina had a mass fraction of 60%~71%, and the composition was reasonable [3], the digestibility was 76%~84%, the main protein was phycocyanin, including phycocyanin (CPC) and phycocyanin [4] (APC), hemoglobin, myoglobin and other functional compounds such as nucleic acid, polysaccharide, glycolipid, gamma-linolenic acid, and beta-carotene. Because of their peculiar function, Spirulina has the function of regulating human physiological function, promoting cell metabolism, enhancing body immunity, slowing cell aging speed, promoting metabolism, resisting radiation tissue damage, assisting in the treatment of cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, obesity and anti-virus and AIDS[5,6].
In recent years, researchers at home and abroad have been studying Spirulina food. The main reason is that Spirulina itself has a strong algal odor, the high loss rate of heat killing protein, poor solubility in solution, and easy to sink particles. Referring to many kinds of literature at home and abroad on the stability and taste of spirulina preparation solution, it is found that the treatment of spirulina products by embedding method [7], fermentation method [8] and enzymatic hydrolysis method [9] has a certain effect, but the products have not been recognized by consumers. Given the above problems, the purpose of this study is to prepare suspension spirulina oral liquid, to explore the optimization of pH, temperature, color protection and stabilizer in the preparation process through sensory evaluation of modulation oral liquid formula, and to use embedding method and UHT high-temperature instantaneous sterilization method to explore more effective methods to reduce protein loss, improve stability and improve the taste by fermentation, and to provide technical reference for deep processing and improve the quality of Spirulina health products by testing its functional indexes.
1.Materials and Methods
1.1Materials and reagents
Spirulina powder Yunnan Natural Fang Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; Tea polyphenols Henan Shangqiu Tuocheng Geng Dao Trading Co., Ltd.; Papaya protease Beijing Xinda Food Addition Co., Ltd.; β-cyclodextrin Henan Zhongtai Food Additives; Lianyungang Kede Chemical Co., Ltd.; Sodium citrate Lianyungang Kede Chemical Co., Ltd.; Pyridol alginate (PGA) Henan Wanbang Industrial Co., Ltd.; sucrose trichloride; salt; xanthan gum; sodium carboxymethyl CMC; wine yeast; honey; sugar in the market.
1.2Instruments and equipment
AD500S-H Laboratory Digital Dispenser Shanghai Onni Instrument Co., Ltd.; FE20PH Meter Mettler-Toledo Instrument Co., Ltd.; LD5-10 Centrifuge Beijing Medical Centrifuge Factory; HH-8 Constant Temperature Water Bath Pot Jiangsu Jintan Rong Hua Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd.; UV-180 UV Spectroradiometer Shanghai Mes instrument Co., Ltd.; PT-20T UHT High-Temperature Instantaneous Sterilization Equipment Shanghai Wardi Automation Equipment Co. Ltd. Ltd.; Anhydroethanol (pure) Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co. Ltd. Ltd.;30% hydrogen peroxide (AR) Chinese medicine group chemical reagent Co., Ltd.; salicylic acid (chemical pure) Chinese medicine group chemical reagent Co., Ltd.; potassium ferricyanide (analytically pure) Tianjin Fengzhou Chemical Reagent Technology Co., Ltd.; ferrous sulfate (analytically pure) Tianjin North Tianyi Chemical Reagent Factory; ferric chloride (analytically pure) Tianjin Fuchen Chemical Reagent Factory; DPPH (>97.0%) Tokyo chemical bead-type community experimental method.
1.3Processflow
raw material → dissolution → high-speed shearing → protease enzymolysis → f- fermentation → embedding → seasoning → adjustment of pH → stabilizer → high-pressure homogenization → UHT sterilization → bottle → inspection of the finished product
1.3.1Operational Points
1.3.1.1Preparation of Spirulina Solution
1.3.1.2The solution of Spirulina was prepared with a concentration of 0.37 mg/mL, adding a certain amount of tea polyphenol powder, tea polyphenols, and Spirulina itself, and the rich β-carotene and vitamin E in Spirulina had a synergistic effect on the antioxidant function of tea polyphenols [10]. The papain was added at 1% of the spirulina mass and the enzymatic hydrolysis time was 2h [11]. enzymatic hydrolysis and high-pressure homogenization (P1) 25 MPa, P2 5 MPa) to make the large particles smaller and then embedded, the wall material selected β-cyclodextrin, the embedding time is 40min [12]. The fermentation was carried out with wine yeast with a fermentation time of 2h and a temperature of 30° C [13].
1.3.1.3 UHT sterilization
Common thermal fungi can easily destroy the nutrients in Spirulina, and the thermal stability of Spirulina needs to be solved. U-HT sterilization not only maintains the nutritive composition of Spirulina juice but also can maintain and improve the aroma of Spirulina juice. UHT is 134° C for 4s [14].
To reduce protein loss, we used the embedding method and the use of tea polyphenols, salt [15] to protect color.
1.3.2Optimizing the Palate Formula
For the addition of honey, sugar osmanthus, citric acid, and whether to choose the optimal formula for fermentation, the sensory evaluation as the index, considering the dosage of each component to take the effect of sensory quality.
1.3.3Stability study
1.3.3.1Effect of temperature on the stability of oral liquid
Spirulina solution was homogeneously embedded in a constant temperature water bath pot at 45,50,55,60,65° C, respectively. The sample was 25 mL in a 25 mL plug test tube and then adjusted to 5.95 after cooling, and the stability of the solution was compared for 30 min,2 h,15 h. The absorbance value at 652 nm,620 nm was measured and calculated by the formula.
1.3.3.2Effect of pH on stability of oral liquid
The solution of Spirulina tea polyphenols was dissolved and homogeneously embedded in a constant temperature water bath at 55° C. The pH of the sample was adjusted to 5.34,5.93,6.30,6.47 and 7.4 after cooling Take 25 mL of 1.7.8 6 in 25 mL of plug tube and compare the stability change of storage for 0.5,2 and 15 hours. The absorbance value of 652 nm and 620 nm is measured and the C-value is calculated by the formula.
1.3.3.3Effect of the Stability of Stabilizer Counterpart Liquid
Adding thickener to spirulina oral liquid is helpful to prevent the particles in the solution from sinking or floating, or condensing each other. After the stabilizer is added, the adsorbed dispersant can keep the stability of the particles at the interface, increase the viscosity of the emulsion and reduce the specific gravity of the two phases, which is an important method to improve the stability of the protein beverage.
xanthan gum, sodium carboxymethyl retinoic acid (CMC), alginate propylene glycol ester (PGA), microcrystalline cellulose were selected as stabilizers, and the optimal stabilizer gradient was selected by using C content and centrifugal precipitation rate as indicators.
1.3.3.4Stabilizer orthogonal test
CMC, PGA, and xanthan gum were selected for orthogonal tests based on the single-factor experiment of stabilizer.
1.3.4Functional testing [16]
Spirulina has been used as a functional food for health management in many parts of the world [17], and scientists at home and abroad have carried out a lot of research on it, but whether the function of prepared oral liquid products after high-temperature sterilization has been destroyed, there are few test reports in the literature. The oral solution is based on the human body’s need for antioxidants to eliminate and resist the body’s free-radical reaction to this requirement and can be prepared by the synergistic action of spirulina, tea polyphenols. phycocyanins in spirulina play an important role as antioxidants in many biological systems [18].
1.3.4.1Force reduction testing
The reduction force was determined by the method of Osawa (Osawa et al.,1981) and slightly changed: take a certain concentration (0.5 to 2.5 mg/mL) of sample 1 mL, add 0.1 mol/L of PBS and 1% potassium ferricyanide solution 2.5 mL each, mix well at 50° C and set aside 20 mi. Then add 2.5 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid to mix, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 10 min, take 2.5 mL of supernatant, add 2.5 mL of distilled water, and 0.1% FeCl32.5 mL, then compare at wavelength 700nm. The strength of the reduction force was proportional to the size of the absorbance, and the blank control group was distilled water, and each operation was repeated three times.
1.3.4.2DPPH free radical scavenging rate
the depth free radical scavenging capacity was determined by the method of Yama (Yama et al .,1998):2 ml of spirulina peptide solution with a certain concentration (0.5– 2.5 mg/ml) was added to 95% ethanol solution of DP-ph with 2ml of 0.2mmol/l, fully mixed and then set aside at room temperature for 30 min. then the absorbance was determined at 517 nm. The ability to scavenge DPPH free radicals is SA.

In the formula:
Blank control :95% ethanol + distilled water;
A1: absorbance of DPPH solution + spirulina-peptide solution;
A2:95% ethanol + spirulina-peptide solution;
A3: absorbance of DPPH solution plus distilled water.
1.3.4.3Determination of hydroxyl radicals
The determination of hydroxyl radical refers to the method of Wu Qiongying (Wu Qiongying et al .,2009) and has been changed: take a certain concentration of sample 2 mL (0.5-2.0 mg/mL), add 2 mL ferrous sulfate (6 mmol/L) in turn,2 mL H2O2(6 mmol/L), and mix for 10 min. then 2 ml salicylic acid (6 mmol/l) was mixed and placed at room temperature for 30 min. the absorbance measured at wavelength 510 nm was ai, aj indicated the absorbance measured when the salicylic acid was replaced by double steamed water, and a0 indicated the absorbance measured by double steamed water instead of the sample. this was a blank control. The hydroxyl radical scavenging rate (%) of the enzyme hydrolysates can be expressed as:
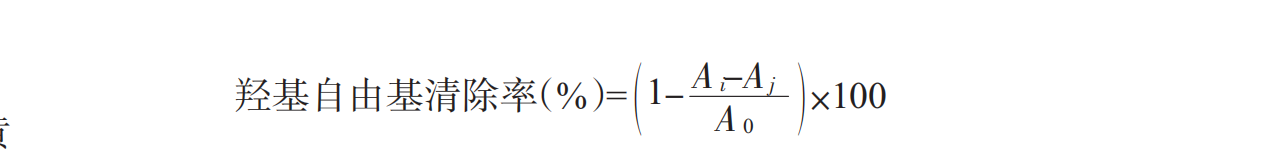
1.3.5Testing indicators
1.3.5.1phycocyanin concentration
The protein in Spirulina is mainly phycocyanin, which can be measured by a UV spectrophotometer, so the difference of the absorption spectrum of phycocyanin in Spirulina is used as the standard. The concentration of phycocyanin is determined by UV-vis at the wavelength of 620nm,652nm, using the following Bennett formula [19,20]:
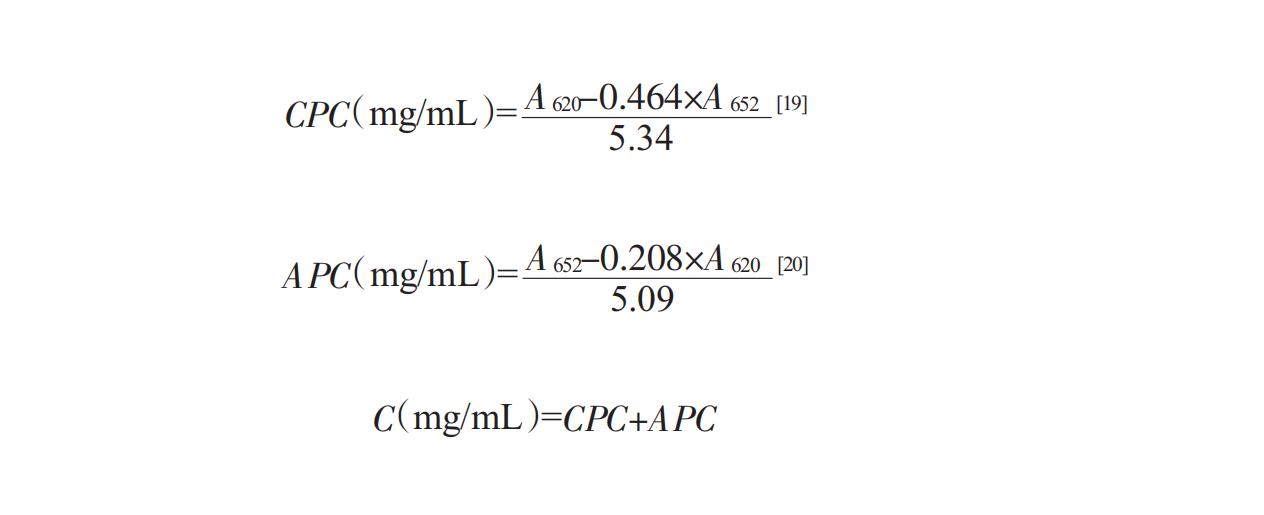
1.3.6Stability factor R%
Add sample solution in centrifuge tube to centrifuge tube 3/4 scale and level, then 3000rmp centrifuge 15min, discard supernatant, accurately measure precipitation weight, precipitation to solution weight ratio, that is, stability coefficient R%:
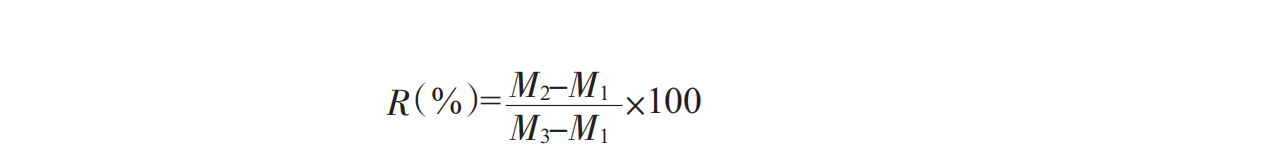
In the formula:
M1 is tube weight;
M2 is precipitation + tube weight;
M3 is solution + tube weight.
According to this empirical formula, the larger the R-value, the greater the settling rate of suspended particles such as proteins in the solution, the worse the suspension of the solution, and the more unstable the oral solution is.
2.Results and Analysis
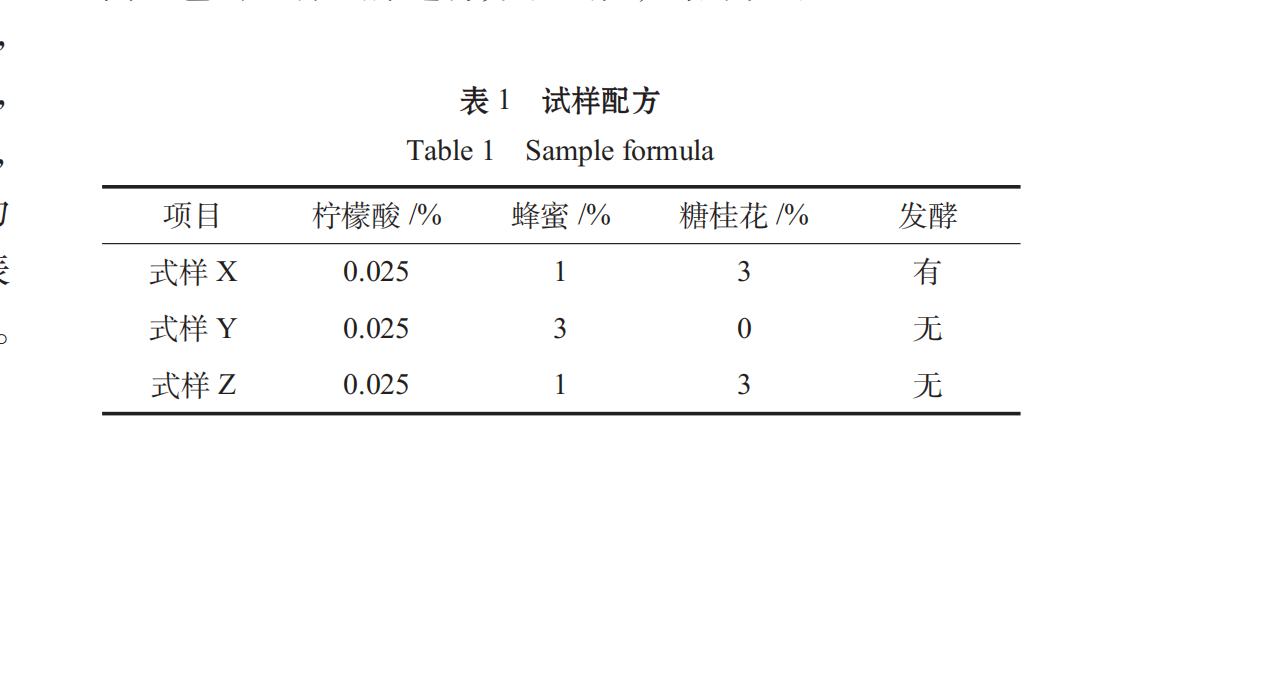
Ten judges were randomly selected from the students of food majors to conduct a comprehensive sensory evaluation of the different formulations of Spirulina oral liquid. The results were as follows:
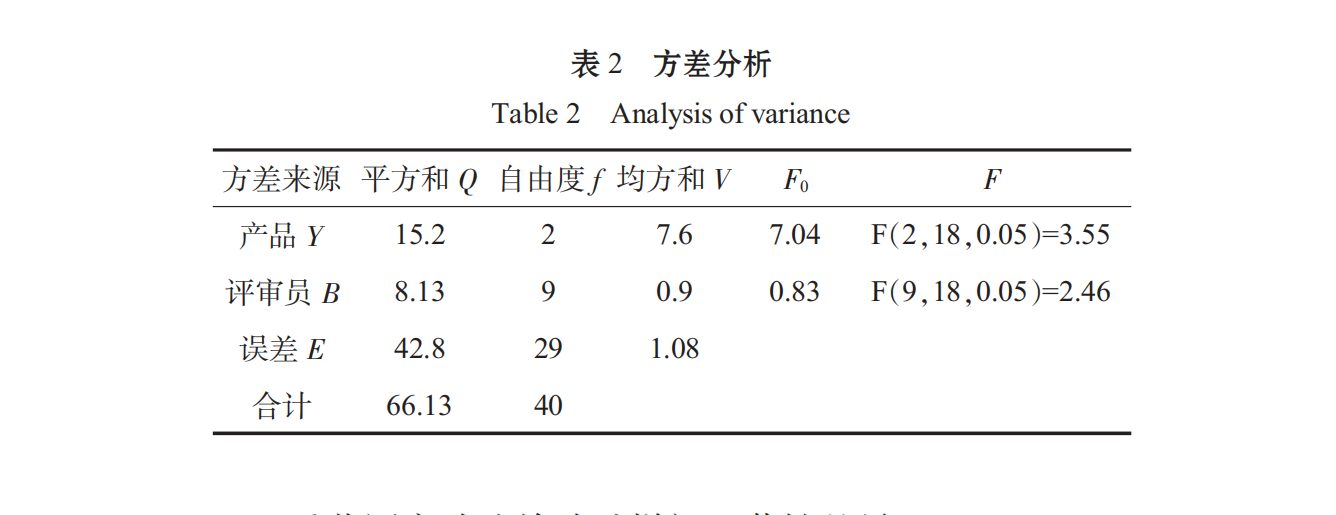
The Significant Difference among the Specimens Tested by the Heavy Range Experiment Method: Average Samples

The standard error in average sample composition:
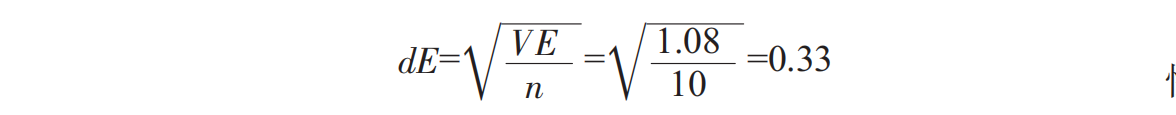
difference studentized range table, studentized range RP, calculated significant difference minimum range rp=rp.de.
Therefore, the significant level of α is 0.05, the difference between sample Y and sample X and Z is significant, and the quality of sample Y is poor.
The addition and fermentation of osmanthus can improve the smell of Spirulina.
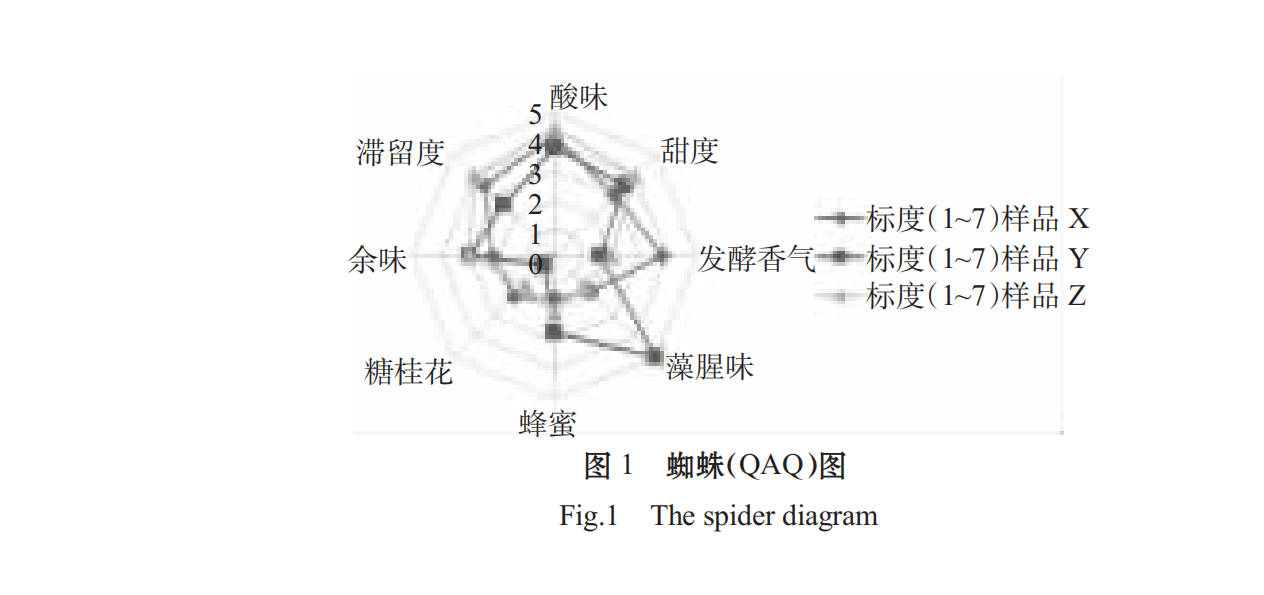
Based on proper sweet and sour ratio, adding proper sugar osmanthus flower can increase the oral liquid taste level, so that the oral liquid has a sweet flavor of osmanthus and is easy to enter. The fermentation process eliminates the smell of Spirulina, which makes it slightly flavored with seaweed, and the fermented aroma produced by wine yeast accords with the popular taste, which makes up for the defect in the oral liquid of Spirulina.
2.1Single Factor Experiment
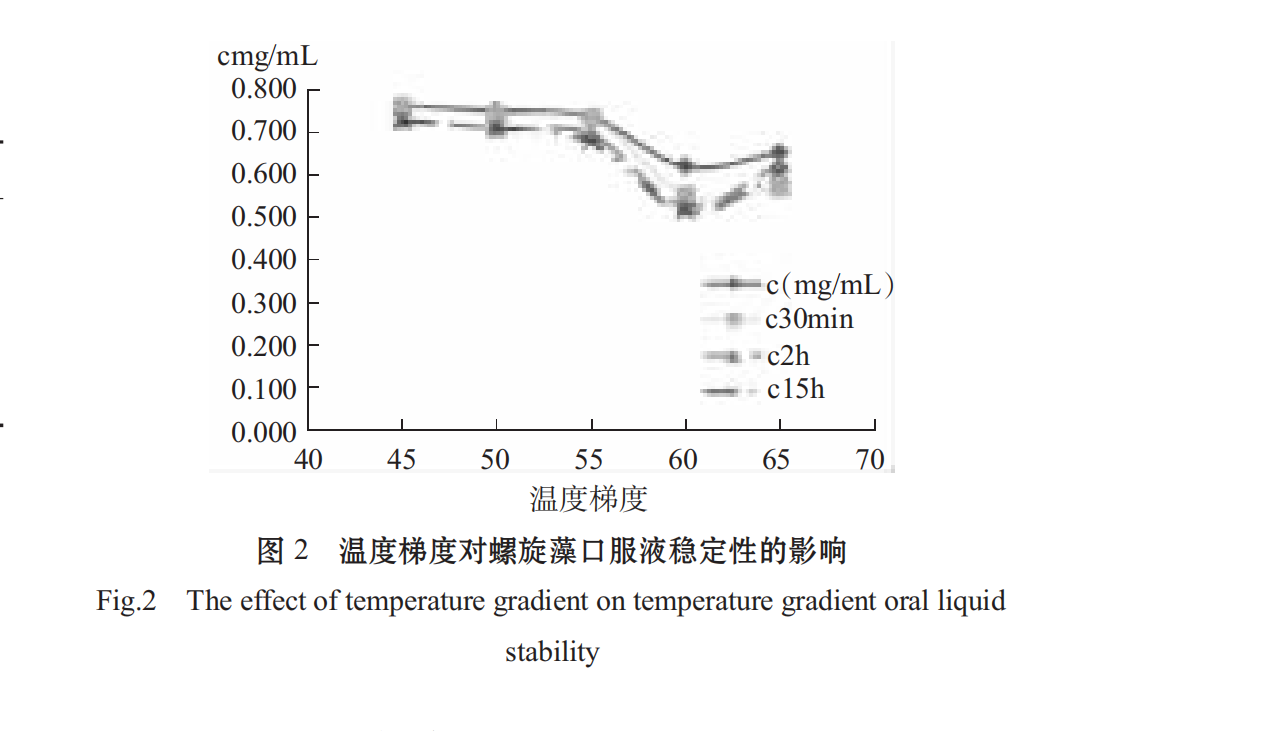
2.1.1Effect of Different Temperatures on Stability of Spirulina Oral Liquid
as can be seen in figure 2, the temperature has a certain effect on the thermal stability of phycochoprotein. the higher the temperature, the higher the loss of phycochoprotein, the obvious decrease of phycochoprotein concentration after 55° c, and the denaturation of phycochoprotein after 70° c, the precipitation leads to a sudden increase in absorbance [21], so spirulina is suitable for low temperature 55° c during processing.
2.1.2Effect of different pH on stability of spirulina oral liquid
Different spirulina growth environments lead to its possible adaptation to different acidity and alkalinity, but most are adapted to acidic conditions. some studies have also shown that the CPC content is more stable under acidic conditions than under neutral or alkaline conditions [22].
through the ph study on the stability of spirulina, from figure 3, it can be seen that the protein stability in oral solution under neutral weak acidity condition is higher than alkaline, and neutral or weak acidity is beneficial to improve the suspension stability of the oral solution. the ph has a great influence on the stability of the solution, and the ph is different, and the stability is different. therefore, when preparing the spirulina oral solution, the ph is controlled to the closing weight. The preparation process should be carried out after the solution is cooled, using citric acid, sodium citrate buffer, pH meter to accurately prepare pH to 5.95.
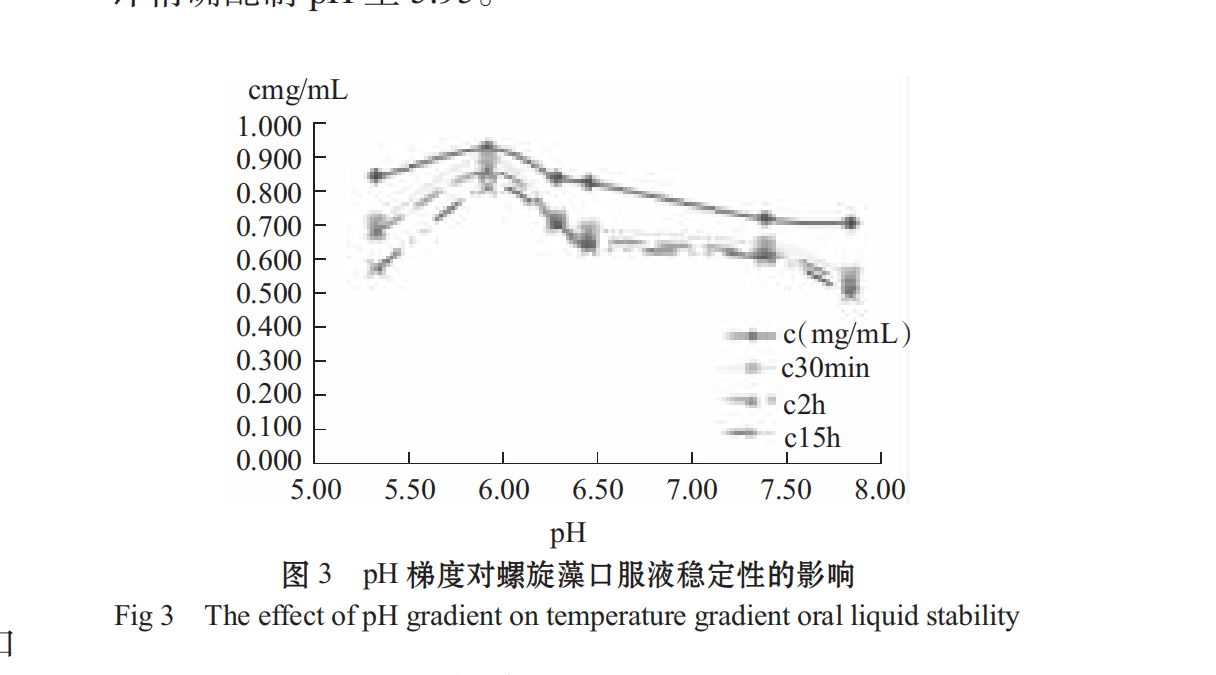
2.1.3Effect of Different Stabilizers on Stability of Spirulina Oral Liquid
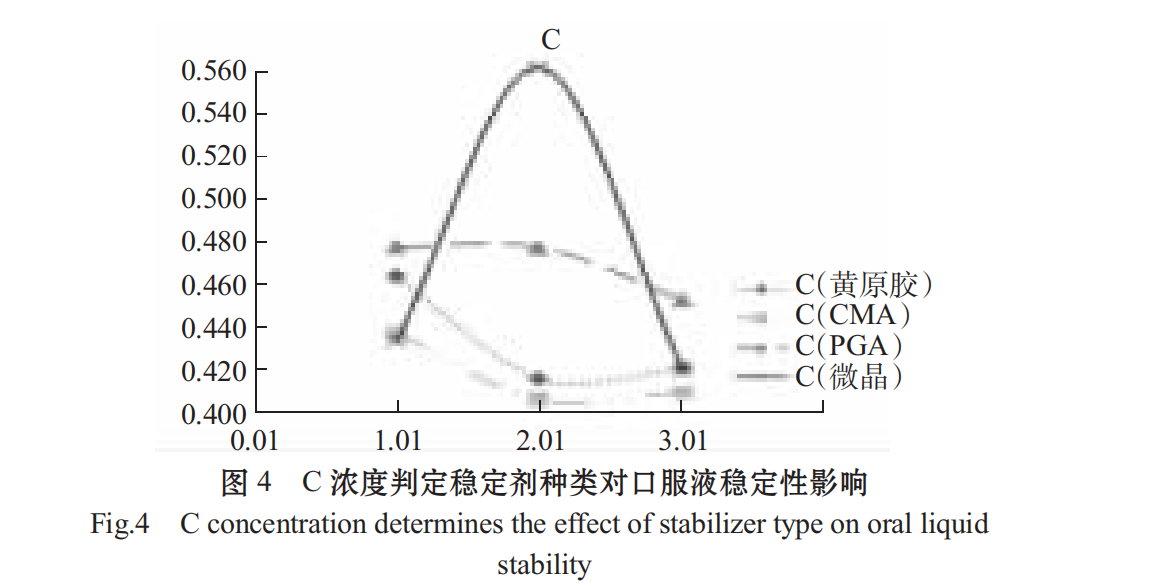
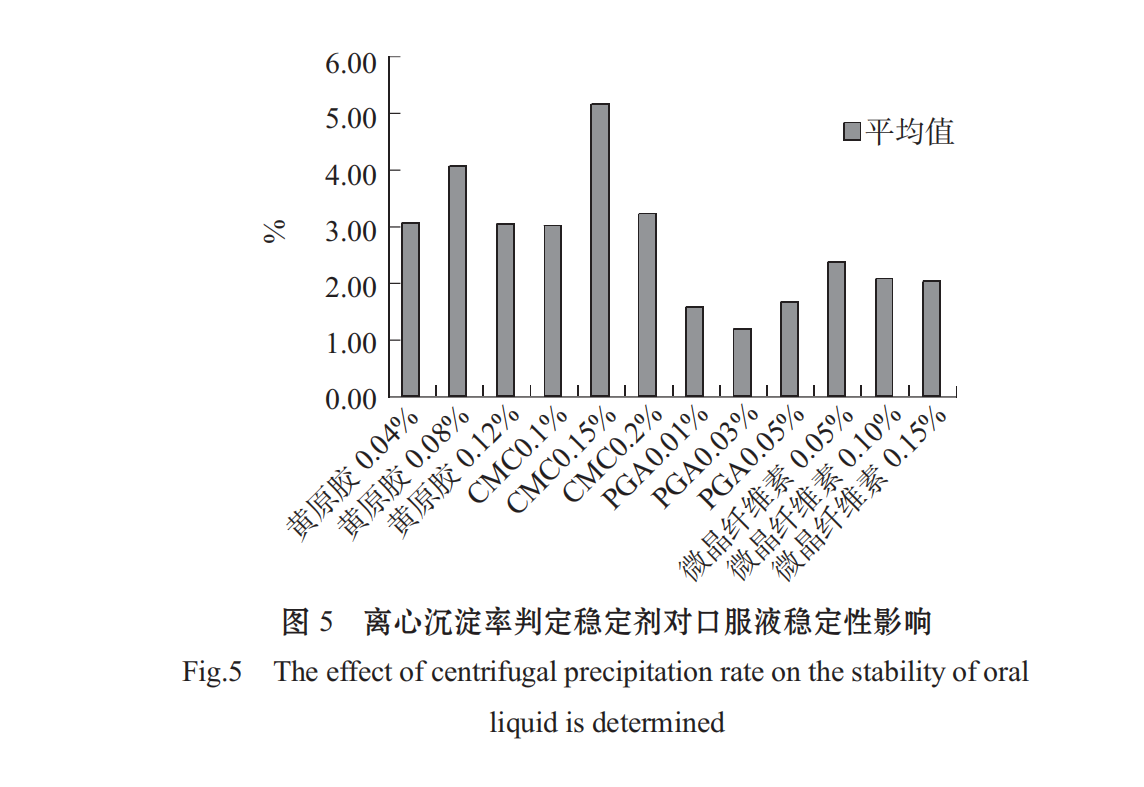
The higher the C content, the smaller the stabilizing effect of the centrifugal precipitation rate (1-R%). As shown in Figs .4 and 5, different stabilizers have a significant effect on the stability of Spirulina oral liquid, the effect is PGA > microcrystalline cellulose > CMC > xanthan in turn. PGA added concentration 0.05%,0.10%,0.1 5% effect is not different, CMC at low concentration of 0.1%, the solution has a better stability effect, xanthan gum at low concentration to the solution stability, choose 0.04%.
2.1.4Stabilizer orthogonal test
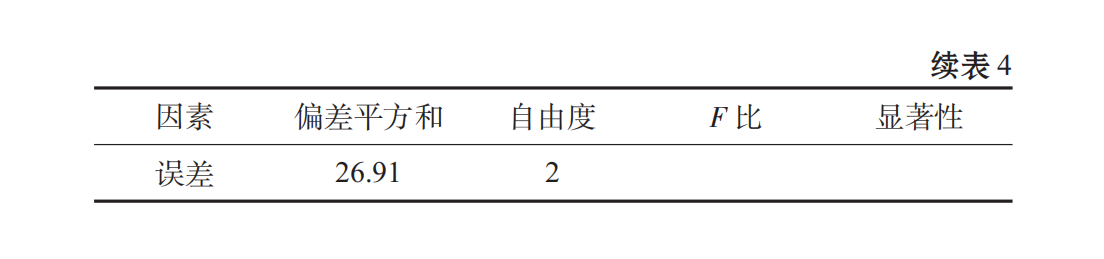
When spirulina granules were broken, the fiber structure of some cell walls was insoluble in water. If the soluble parts were extracted, the protein content was too low, which was not consistent with the original intention of experimental research. From Table 3, Table 4, we can see that the primary and secondary order of the factors affecting the stability of oral liquid is C > B > A, that is, PGA > Xanthan gum > CMC, and the best combination is A3B2C. It has been shown that the beverage stability coefficient R of this scheme is 97.025%.
2.2 Functional testing
Through the reduction force, DPPH free radical scavenging force, hydroxyl radical, and the results are as follows:
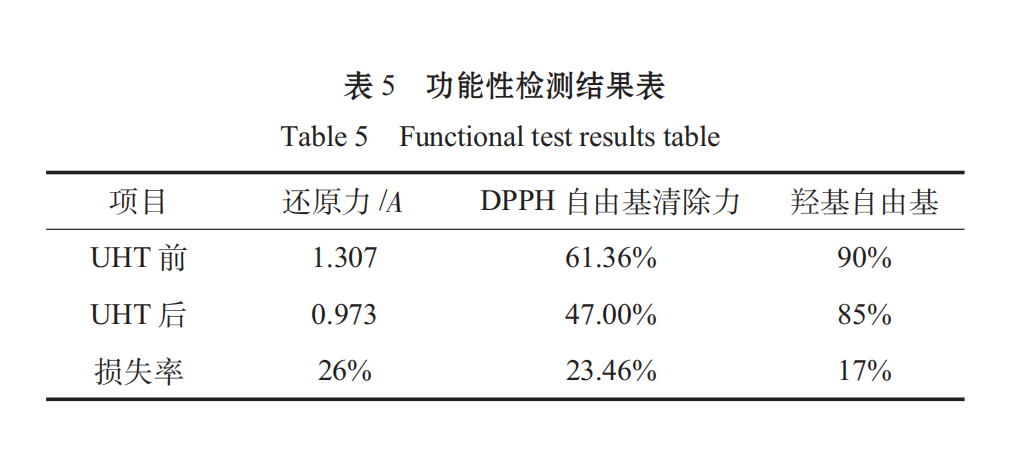
spirulina as a health food, its value is more reflected in its health care effect. after determination, the antioxidant functional loss after UHT is about 20%, and the overall function meets the standard.
3.Result
3.1Spirulina powder has a heavy taste, which is buried by fermentation and β-cyclodextrin Add sucralose, osmanthus, salt, citric acid Taste, wine yeast fermentation, through the orthogonal test to optimize the formula, to get wind Good taste, blue-green slightly turbid oral liquid.
3.2 Spirulina thermal stability poor, phycocyanin color (blue) through. Use tea polyphenols, salt, and other color protection, and after β-cyclodextrin embedded use, UHT sterilization minimizes protein loss and maintains solution turquoise.
3.3The solubility of Spirulina was poor. The suspension oral solution passed orthogonal test The optimum proportion of stabilizers was determined to be 0.06% xanthan gum and 0.12% CMC. PGA0.08%。
3.4 Before and after UHT contrast protein loss rate 17.26%, functional loss rate. It’s 20% left. Spirulina oral liquid has a good function.
References
[1] RI CHMOND A S. Microalgae biotechnology[M].Cambridge Univ Press,1988:1-2.
[2]M Salazar, E Madrigal, L E Ruiz, et Subchronic toxicity study in mice fed Spirulina maxima[J].J Ethnophamnacol, 1998, 62(3): 235-241.
[3]LiuHui, Liu Pengju, Zhang Shaobin,. Studies and applications of spirulina cholin [J]. Agriculture in Anhui Science ,2006,34(21):546 3-5464.
[4]Fu Guiming, Wan Yin, Lu Yingfeng. development of cyanobacteria nutrient oral liquid [j]. Food Industry Technology,2008(4):165-168.
[5]ZHANG Y M, CHEN. A simple method for efficient separation and purification ofc-phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis[J].Biotechnology Techniques, 1999, 13: 601-603.
[6]LuXiaoling, Yao functional components of Spirulina, and their peculiar functions [J. Journal of Tianjin Institute of Light Industry,1995(2):23-27.
[7]Yang Poria cocos spirulina health beverage preparation technology study [J]. Chinese Food and Nutrition,2009(3): 42-43.
[8]Wei Yucui, Xie Ding, Liu Yongle, Optimization of the deodorization process of Spirulina and the development of its enhanced rice flour [J]. Food and Machinery,2011 (1):136-139.
[9]Wang Chen, Liu. enzymatic hydrolysis of Spirulina proteins [J]. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2008, 36(31):13485-13487.
[10]development of tea polyphenol spirulina tablets [d]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University,2009.
[11]Wang Chen, Zhang Yan. Study on blending process and stability of spirulina oral liquid [J]. Food Science ,2009,30(12):90-93.
[12]Wei Zhencheng, Zhang Yan, Chi Jian. Optimization of the process formulation of spiral clear juice beverage [J].Guangdong Agricultural Science;2006(11).
[13]Yang Hui, Fang Sui, Zou Xia, screening of spirulina deodorization processes [j]. Food research and development,2009(7): 106-110.
[14]WuQiong, Feng Weimin, Jiang Effect of different sterilization methods on mulberry juice quality [J]. Food Science ,2016,37(9):144-149.
[15]RATANA Chaikalahan, Nattayaporn Chirasuwan, Boosya Bunnag. Stability of phycocyanin extracted from Spirulina sp Influence of temperature pH and preservatives[J].Process Biochemistry, 2012, 47: 659-664.
[16]Ma Preparation and antioxidant properties of spirulina peptides [D]. Taiji- n: Shandong Agricultural University, 2016.
[17]Wang Wenbo, Sun Jianguang, Xu. Detection and immune function of active substances in Spirulina [J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 23(1):54-61
[18]LiuLingjie, Chen Weiwei, Liang Di, progress in the study of the nutritional health care effect and deodorization of spirulina [j]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Prescriptions 23(2):213-219.
[19]PatelA, Mishra S, Pawar R, Ghosh K.Purification and characterization of C-phycocyanin from cyanobacterial species of marine and freshwater habitat[J].ProteinExp Purif,2005(40):248-255.
[20]Jespersen L, Stromdahl LD, Olsen K, et al. Heat and light stability and light stability of three natural blue colorants for use in confectionery and beverages[J].Eur Food Res Technol, 2005(220): 261-266.
[21]Zhang Hou Sen Ma Hai. stability test study of phycocyanin in blue spirulina velutipes [j]. Food Research and Development, 2005, 6, 74-76.
[22]Liu J C, Hou W C, Lee S Y, et. Antioxidant effects and UVB products fermented with lactic acid bacteria[J]. Process Biochem,2011(46): 1405-1410.
